MoEngage is an intelligent customer engagement platform that allows you to effectively engage with your customers throughout their product journey. It allows you to track and map your customer life-cycle across various touchpoints, and optimize their customer experience at each stage.
RudderStack supports MoEngage as a destination to seamlessly send your event data in real-time.
Getting started
RudderStack supports sending event data to MoEngage via the following connection modes:
| Connection Mode | Web | Mobile | Server |
|---|---|---|---|
| Device Mode | Supported | Supported | - |
| Cloud Mode | Supported | Supported | Supported |
http(s)://cdn.moengage.com/webpush/moe_webSdk.min.latest.js domain. Based on your website's content security policy, you might need to allowlist this domain to load the MoEngage SDK successfully.Once you have confirmed that the platform supports sending events to MoEngage, perform the steps below:
- From your RudderStack dashboard, add the source. From the list of destinations, select MoEngage.
- Assign a name to the destination and click Continue. You should then see the following screen:
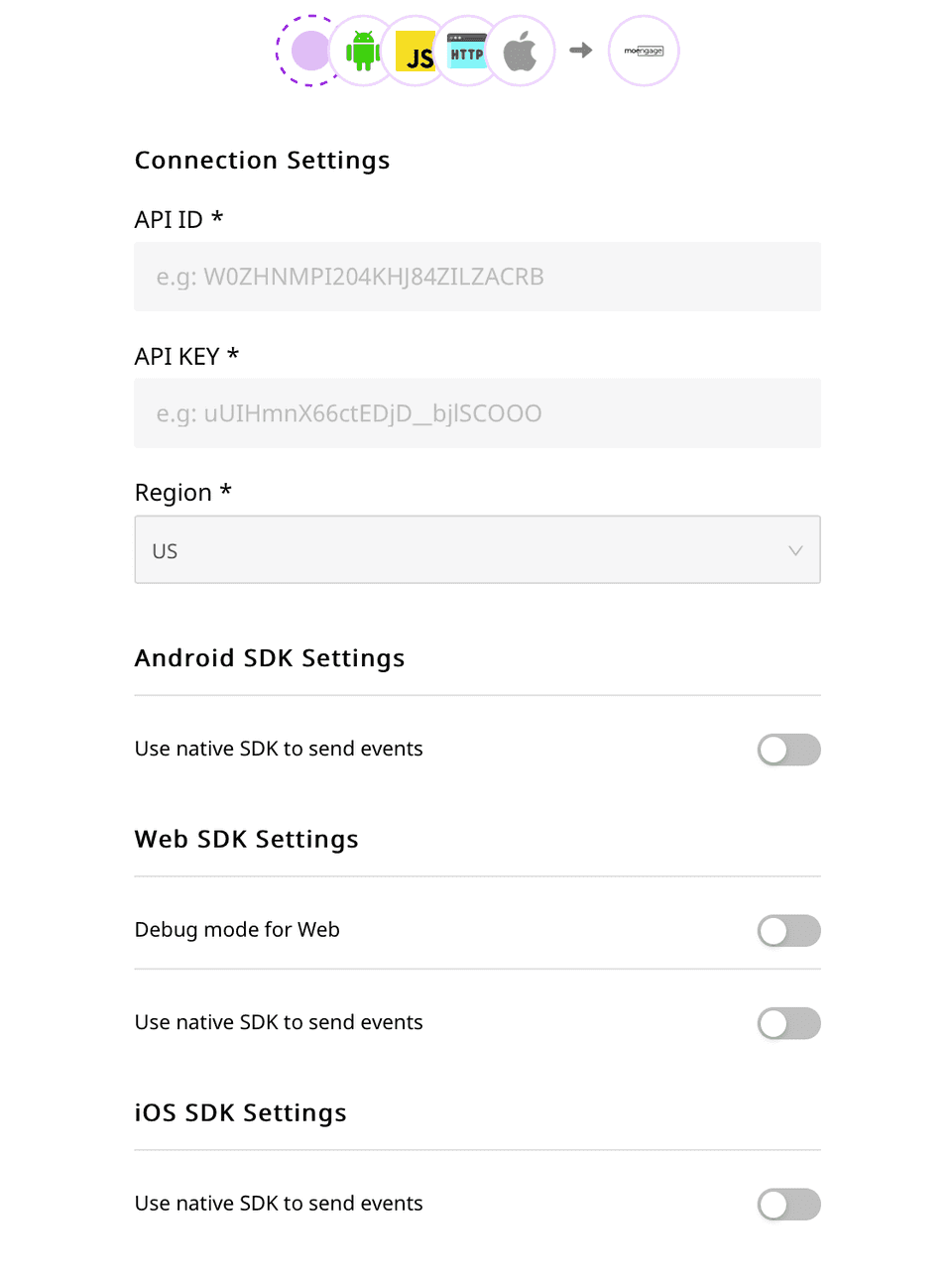
In the Connection Settings on the RudderStack dashboard, enter the MoEngage API ID, API Key, and Region, as shown above.
Adding device mode integration
Once you add MoEngage as a destination in the RudderStack dashboard, follow these steps to add it to your project, depending on your integration platform:
- Go to your
Podfileand add theRudder-Moengageextension:pod 'Rudder-Moengage' - After adding the dependency followed by
pod install, you can add the imports to yourAppDelegate.mfile, as shown:#import "RudderMoengageFactory.h" - Finally, change the initialization of your
RudderClient, as shown:RudderConfigBuilder *builder = [[RudderConfigBuilder alloc] init];[builder withDataPlaneUrl:DATA_PLANE_URL];[builder withFactory:[RudderMoengageFactory instance]];[RudderClient getInstance:WRITE_KEY config:[builder build]];
- Install
RudderMoEngage(available through CocoaPods) by adding the following line to yourPodfile:pod 'RudderMoEngage', '~> 1.0.0' - Run the
pod installcommand. - Then, import the SDK depending on your preferred platform:import RudderMoEngage@import RudderMoEngage;
- Next, add the imports to your
AppDelegatefile under thedidFinishLaunchingWithOptionsmethod, as shown:let config: RSConfig = RSConfig(writeKey: WRITE_KEY).dataPlaneURL(DATA_PLANE_URL)RSClient.sharedInstance().configure(with: config)RSClient.sharedInstance().addDestination(RudderMoEngageDestination())RSConfig *config = [[RSConfig alloc] initWithWriteKey:WRITE_KEY];[config dataPlaneURL:DATA_PLANE_URL];[[RSClient sharedInstance] configureWith:config];[[RSClient sharedInstance] addDestination:[[RudderMoEngageDestination alloc] init]];
- Open your
app/build.gradle(Module: app) file and add the following:repositories {mavenCentral()} - Add the following under the dependencies section:// RudderStack Android and MoEngage SDKsimplementation 'com.rudderstack.android.sdk:core:[1.0,2.0)'implementation 'com.rudderstack.android.integration:moengage:2.0.0'// For MoEngage core SDK initialisationimplementation("com.moengage:moe-android-sdk:12.5.04")// Firebase messaging dependencyimplementation 'com.google.firebase:firebase-messaging:23.1.1'// If you don't have Gson included alreadyimplementation 'com.google.code.gson:gson:2.8.9'
- Also, add the below plugin after
buildscript:// For Push Notificationapply plugin: 'com.google.gms.google-services' - Open your
build.gradle(Module: Project) file and add the following in thebuildscriptdependencies:// For Push Notificationbuildscript {dependencies {classpath 'com.google.gms:google-services:4.3.14'}} - Initialize the RudderStack SDK in the
Applicationclass'sonCreate()method, as shown:// initializing Rudder SDKval rudderClient = RudderClient.getInstance(this,WRITE_KEY,RudderConfig.Builder().withDataPlaneUrl(DATA_PLANE_URL).withFactory(MoengageIntegrationFactory.FACTORY).build()) - Initialize the MoEngage SDK in the
Applicationclass'sonCreate()method:// initializing MoEngage SDK and "XXXXXXXXXXX" is the APP ID from the dashboard.val moEngage = MoEngage.Builder(this, "XXXXXXXXXXX").configureLogs(LogConfig(LogLevel.VERBOSE, false)).build()MoEngage.initialiseDefaultInstance(moEngage)
- Add the RudderStack-MoEngage module to your app by running the following command:npm install @rudderstack/rudder-integration-moengage-react-native// OR //yarn add @rudderstack/rudder-integration-moengage-react-native
- Import the above module and add it to your SDK initialization, as shown:import rudderClient from "@rudderstack/rudder-sdk-react-native"import moengage from "@rudderstack/rudder-integration-moengage-react-native"const config = {dataPlaneUrl: <DATA_PLANE_URL>,trackAppLifecycleEvents: true,withFactories: [moengage],}rudderClient.setup( <WRITE_KEY> , config)
- Add the following under the dependencies section of the
android/app/build.gradle(Module: app) file in the Android folder of your React Native project:implementation 'com.rudderstack.android.sdk:core:1.+'implementation 'com.rudderstack.android.integration:moengage:1.0.0'implementation 'com.moengage:moe-android-sdk:10.5.00'//jet pack library required by moengageimplementation 'androidx.core:core-ktx:1.3.2'implementation 'androidx.appcompat:appcompat:1.2.0'implementation 'androidx.lifecycle:lifecycle-process:2.2.0'//firebase messaging dependencyimplementation 'com.google.firebase:firebase-messaging:21.0.0'// if you don't have Gson included alreadyimplementation 'com.google.code.gson:gson:2.8.6' - In the
android/build.gradle(Module: Project) file, add the following:repositories {mavenCentral()} - Add the following in the
buildscriptdependencies inandroid/build.gradle(Module: Project) file:// For Push Notificationbuildscript {dependencies {classpath 'com.google.gms:google-services:4.3.4'}} - Also, add the following plugin at the top of
android/app/build.gradle(Module: app):// For Push Notificationapply plugin: 'com.google.gms.google-services' - Initialize the MoEngage SDK in the
Applicationclass'onCreate()method, as shown:// MoEngage SDK initialisation: Replace "xxxxxxx" with your APP ID.MoEngage moEngage = new MoEngage.Builder(MainActivity.this.getApplication(), "xxxxxxx").enableLogs(LogLevel.VERBOSE).build();MoEngage.initialise(moEngage);
Identify
To identify a user to MoEngage, you need to call the identify API.
MoEngage needs a unique identifier to identify a user. So, if you provide userId in your identify call, RudderStack passes it as that customer_id . Otherwise, it sends an anonymousId if a userId is not present.
You can also create a new user property or update existing user properties of the users using the identify API.
A sample identify call is as shown:
rudderanalytics.identify("name123", { name: "Name Surname", first_name: "Name", last_name: "Surname", email: "name@surname.com", createdAt: "Thu Mar 24 2020 17:46:45 GMT+0000 (UTC)",})Identify api will be used to Login the user into MoEngage in Device Mode
MoEngage Reserved Properties
The following property names are reserved by MoEngage:
namefirst_namelast_nameemailagegendermobiletransactionsrevenuemoe_unsubscribe
You may create custom properties but you should not create properties with the following names "id", "_id", or "" .
Identifying a Device to MoEngage
You can also identify a device to MoEngage , using the identify API. With this API, you can create new properties or update the existing properties of the device.
A sample call for identifying device is as shown:
rudderanalytics.identify("name123", { context: { device: { id: "7ase32188a4dab669f", manufacturer: "Apple", model: "IOS SDK built for x86", name: "generic_x86", token: "devtoken", type: "ios", }, },})Track
To track your users' actions, you can use the RudderStack track API. You can call track with eventname and the associated properties.
A sample track call is as shown:
rudderanalytics.track("Order Completed", { checkout_id: "C324532", order_id: "T1230", value: 15.98, revenue: 16.98, shipping: 3.0, coupon: "FY21", currency: "INR", products: [ { product_id: "product-mixedfruit-jam", sku: "sku-1", category: "Food", name: "Food/Drink", brand: "Sample", variant: "None", price: 10.0, quantity: 2, currency: "INR", position: 1, value: 6.0, typeOfProduct: "Food", url: "https://www.example.com/product/bacon-jam", image_url: "https://www.example.com/product/bacon-jam.jpg", }, ],})Alias
The Alias api is used to merge two different profiles of a same user into a single profile.
Alias call can be done only through mobile sdks.
For more information, refer to our RudderStack Events Specification guide.
- Run the following command to implement the
aliasmethod in your iOS project:[[RSClient sharedInstance] alias:@"newId"];
rudderClient.alias("newId")Reset
The reset method resets the previously identified user and the related information. For more information, refer to our RudderStack Events Specification guide.
reset method in your iOS project:[[RSClient sharedInstance] reset];reset method in your Android project:rudderClient.reset()RESET api is applicable only for Device Mode Connections
Supported mappings
RudderStack maps the following properties to the MoEngage properties before sending them over MoEngage's HTTP API.
| RudderStack property | MoEngage property |
|---|---|
pushPreference | push_preference |
active | active |
userId | customer_id |
name | name |
firstname/first_name/firstName | first_name |
lastname/last_name/lastName | last_name |
email | email |
age | age |
gender | gender |
mobile | mobile |
source | source |
createdAt | created_time |
last_seen/lastSeen | last_seen |
transactions | transactions |
revenue | revenue |
moe_unsubscribe/moeUnsubscribe | moe_unsubscribe |
event | action |
properties | attributes |
Configuring Push Notifications
- To send push notifications in iOS an APNS certificate needs to be created and has to be converted to
.pemfile. - This
.pemfile needs to be uploaded in the MoEngage dashboard. - In the target app turn on App Groups and enable one of the App group ids, in case if you don't have an App Group ID then create one. The name of your app group should be
group.{bundle id}.MoEngage. - Turn on Background mode and set/enable Remote Notification.
- Turn on push notification capabilities in your app.
- Before initializing add
[MoEngage setAppGroupID:<your app group id>]; - In case if you would like to keep the notifications even after the App Launch then :
[MoEngage sharedInstance].disableBadgeReset = true;
In-App messaging
In-app messaging is a type of mobile messaging where the notification is displayed within the app. Some examples include popups, yes/no prompts, interstitials, and more. To implement this follow this guide: InApp NATIV.- To send push notifications in iOS, an APNS certificate needs to be created and converted to a
.pemfile. This.pemfile needs to be uploaded in the MoEngage dashboard. - Enable Background mode by navigating to Targets > Select Your App > Signing & Capabilities > Select Background Modes. Then, check Remote notifications.
- Then, in your
plistfile, add theMoEngageAppDelegateProxyEnabledkey and set it tofalseto disable swizzling. - Finally, implement the relevant methods in your
AppDelegatefile by referring to this section. - To keep the push notifications even after app launch, you can call the below method:MoEngage.sharedInstance().setDisableBadgeReset(true)[[MoEngage sharedInstance] setDisableBadgeReset:true];
build.gradle file.Adding meta for push notification
To show push notifications you need to add the notification small icon and large icon along with the AppId to theMoEngage.Builderval moEngage = MoEngage.Builder(this, "XXXXXXXX") .setNotificationSmallIcon(R.drawable.icon) .setNotificationLargeIcon(R.drawable.ic_launcher) .build()MoEngage.initialise(moEngage)- Registration for Push, i.e. generating push token.
- Receiving the Push payload from Firebase Cloud Messaging(FCM) service and showing the notification on the device. The above can either be handled by the application or MoEngage SDK. There is some configuration required based on whether the above-mentioned things are handled by the application or SDK.
Push Registration and Receiving handled by App
By default, MoEngage SDK attempts to register for push token, since your application is handling push you need to opt-out of SDK's token registration.
How to opt-out of MoEngage Registration?
To opt-out of MoEngage's token registration mechanism call in the optOutTokenRegistration() on the MoEngage.Builder as shown below
val moEngage = MoEngage.Builder(this, "XXXXXXXX") .setNotificationSmallIcon(R.drawable.icon) .setNotificationLargeIcon(R.drawable.ic_launcher) .configureFcm(FcmConfig(false)) .build()MoEngage.initialise(moEngage)Pass the Push Token To MoEngage SDK
The Application would need to pass the Push Token received from FCM to the MoEngage SDK for the MoEngage platform to send out push notifications to the device. Use the below API to pass the push token to the MoEngage SDK.MoEFireBaseHelper.getInstance().passPushToken(applicationContext, token)Passing the Push payload to the MoEngage SDK
To pass the push payload to the MoEngage SDK call the MoEngage API from the `onMessageReceived()` from the Firebase receiver. Before passing the payload to the MoEngage SDK you should check if the payload is from the MoEngage platform using the helper API provided by the SDK.if (MoEPushHelper.getInstance().isFromMoEngagePlatform(remoteMessage.data)) { MoEFireBaseHelper.getInstance().passPushPayload( applicationContext, remoteMessage.data )} else { // your app's business logic to show notification}Push Registration and Receiving handled by SDK
Add the below code in your manifest file within the application tag<service android:name="com.moengage.firebase.MoEFireBaseMessagingService"> <intent-filter> <action android:name="com.google.firebase.MESSAGING_EVENT" /> </intent-filter></service>FirebaseEventListener and registering for a callback in the Application class' onCreate()using MoEFireBaseHelper.getInstance().setEventListener()In-App messaging:
In-app messaging is a type of mobile messaging where the notification is displayed within the app. Examples include popups, yes/no prompts, interstitials, and more. To implement this follow: InApp NATIV- Go to Web Push Settings.
- Under Web fill in the details as required.
- For HTTPS Web Push to work, you need to host two files in the
rootdirectory of your web server. - After clicking **SAVE**, proceed to download
serviceworker.jsfile. Under Web Push Settings. - In case you already have your own serviceworker.js add :importScripts("https://cdn.moengage.com/webpush/releases/serviceworker_cdn.min.latest.js")
- HTTP : Select a sub-domain. For more details follow the guidelines from MoEngage.
- Open the
androidfolder of your React Native app and follow all the steps listed in theAndroidtab of the Configuring Push Notifications section. - Open the
iosfolder of your React Native app and follow all the steps listed in theiOStab of the Configuring Push Notifications section.
Debugging in the web SDK
From the RudderStack dashboard, turn on the debug mode to get debug logs. The events will be seen under the Test section of the particular app in MoEngage.
Timezone offset for cloud mode
Track
MoEngage allows sending the time at which the event occurred and calculates the user local time by taking two parameters. current_time and user_timezone_offset where the current_time is UTC Time at which the event happened, and user_timezone_offset is the difference in seconds between the user local time and UTC.
The RudderStack transformer maps the current_time to timestamp or originalTimestamp value from the event payload sent to Rudder server. This value should be passed in UTC.
The user_timezone_offset is mapped to timezone field present under the context object of the event payload. This value should be passed as tz string. Rudder mobile SDKs populate the timezone field by itself. But for other sources like server like SDKs, HTTP api, the timezone needs to be set explicitly in every request.
Example payload:
{ "type": "track", "event": "Email Replied", "sentAt": "2020-12-02T11:30:33.262Z", "context": { "library": { "name": "analytics-node", "version": "0.0.3" }, "timezone": "Asia/Kolkata" }, "rudderId": "87a40cf3-f6d8-4675-bc01-7854ab4486ec", "_metadata": { "nodeVersion": "10.22.0" }, "messageId": "node-7519b5f2fcacca521c7a9e8ddb9fc09c-c273004b-6968-422d-a511-440b6db24403", "properties": { "details": "list of details" }, "anonymousId": "anony11111111111", "originalTimestamp": "2020-12-02T11:30:33.259Z"}Identify
MoEngage accepts user creation time for its user endpoint. This is reflected as first_Seen in their dashboard.
The RudderStack transformer maps the created_time from the createdAt spec'd traits in our payload. The value should be in the ISO 8601 format. If the value is not in proper format or not present, MoEngage will put in the value by itself.
An example payload is as shown:
{ "type": "identify", "sentAt": "2020-12-02T13:04:05.953Z", "traits": { "city": "Bangalore", "name": "lolo", "email": "lolo@website.com", "country": "India", "createdAt": "2020-12-02T12:29:53.872Z" }, "userId": "111its111", "context": { "traits": { "city": "Bangalore", "name": "lolo", "email": "lolo@website.com", "country": "India", "createdAt": "2020-12-02T12:29:53.872Z" }, "library": { "name": "analytics-node", "version": "0.0.3" } }, "rudderId": "754fe90e-89fb-4d71-9d11-3ec2b91b5777", "_metadata": { "nodeVersion": "10.22.0" }, "messageId": "node-1a585828272cf1116407aaf6be3921f2-65c1670e-f4e1-4283-a7a5-0a60825c4f83", "originalTimestamp": "2020-12-02T13:04:05.951Z"}FAQs
Where can I find my MoEngage API ID and API KEY?
You can find your MoEngage API ID and API KEY in your moengage.com account under Settings > APIs > DATA API Settings.
Where can I see the events that are going to MoEngage?
If your app is in debug mode then you can see under Test otherwise you can see under Live. Go to For developers --> Recent Events.
Contact us
For more information on the topics covered on this page, email us or start a conversation in our Slack community.